NF-KAPPA B ACTIVATION ASSAY KIT | NFKB, NF-kB, NF-{kappa}B, Nuclear Factor-Kappa B | Part NFKB-2
 Click to enlarge |
|
NF-kappa B (NFkB) Activation Assay Kit
|
NF-kB (NF-{kappa}B, Nuclear Factor-kappa Beta) Assay Kit
|
|
NF-kB (NF-kappa B) Activation Assay
|
|
Following stimuli that elicit the NF-kB pathway, the IkB inhibitory subunit of the NF-kappa B complex is phosphorylated, ubiquitinated and degraded, exposing nuclear targeting signals in the transcription factor subunits of the NF-kappa B complex. The NF-kappa B transcription factor subunits, p65 and p50, with exposed nuclear targeting signals, then translocate into the nucleus. The NF-kappa B assay kit provides an accurate quantitative estimate of NF-kappaB activation by measuring p65 (RelA) protein that has been translocated to the nucleus.
Protocol Synopsis
The NF-kB assay kit isolates nuclear and cytoplasmic protein fractions, with concentrated p65(RelA) protein partitioned in the nuclear fraction. Western blots, that are developed with antibodies that are included with this kit, are then employed to detect and quantitate p65(RelA). To fractionate cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction, cells (or tissues after homogenization) are first processed with the "Cytoplasmic Fractionation Reagent (Part CER-1)." The cell suspension is briefly centrifuged in a microcentrifuge, generating the cytoplasmic fraction in the supernatant. A resulting pellet is washed in the Cytoplasmic Fractionation Reagent and then extracted with the "Nuclear Fractionation Reagent (Part No. NER-1)." Aliquots of each fraction are resolved in Western blots, with consecutive lanes loaded to display the total cell lysate, cytoplasmic fraction and nuclear fraction. The ratio of p65(RelA) protein in the nuclear relative to the cytoplasmic fraction provides a calculation of NF-kappa B activation.
|
|
|
|
Contents
|
Part
|
Description
|
Volume
|
|
1.
|
CER-1
|
Cytoplasmic Fractionation Reagent
|
55 ml
|
|
2.
|
NER-1
|
Nuclear Fractionation Reagent
|
3.5 ml
|
|
3.
|
DTT
|
Dithiothreitol
|
(solid)
|
|
4.
|
p65Ab
|
Rabbit IgG antibody to p65(RelA)
|
100 µl
|
|
5.
|
G-HRP
|
Goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP
|
50 µl
|

|
Number of Kits
|
Price
|
|
1
|
$419
|
|
2
|
$794
|
|
3
|
$1125
|
|
Antibody to p65(RelA) for Western Blots (provided with the kit)
Antibody to p65(RelA) for Western blot is provided in 100 microliter aliquots (rabbit polyclonal, IgG; applicable at suggested 1:400 dilution). The antibody is reactive toward human, mouse, rat, and bovine p65. A matched goat- anti-rabbit IgG-HRP antibody is included in the kit for Western blot detection.
|
|
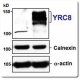
NFKB-2 Kit Data
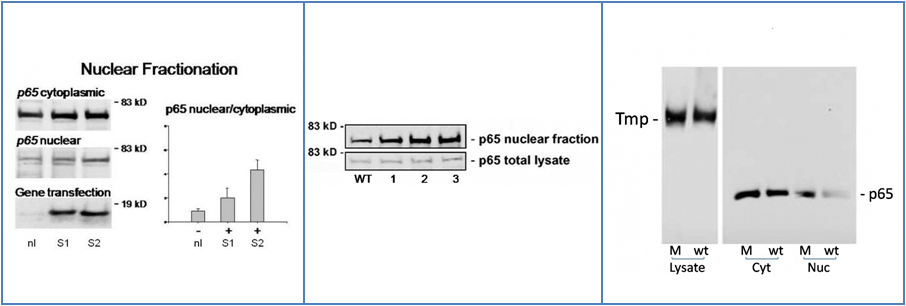
Data revealing nuclear and cytoplasmic fractionation, NF-kappa B activation and reactivity of the provided p65 antibody. All data were derived from transfected HEK293 cells. The images below can be enlarged by right clicking and selecting view image (Mac: Ctl click, select view image).
|
|
Figure A: Western blot and quantitative analysis revealing NF-kappa B activation in three experimental repetitions elicited by overexpression of SNP variants of a gene associated with a neurological disease. Lane 1 in the Western blot and the corresponding bar chart reflect the mock transfection control (nl). Lane 2 in the Western blot and the corresponding bar chart reveal mutant variant SNP-1 expression (S1). Lane 3 in the Western blot and bar chart reveal the NF-kappa B response to SNP-2 (S2) expression. Western blot data display elevated levels of p65 subunit protein in the nuclear fraction corresponding to expression of SNPs 1 and 2, implicating cellular stress and NF-kappa B activation. Figure B: An independent, identical experiment to that displayed in Figure 1, revealing elevated translocation of p65 into the nuclear fraction following transfection of SNP variants 1 to 3 of the gene associated with a neurological disease. Comparisons were done with p65 protein levels in nuclear fractions relative to p65 levels in total cell lysate. Transfection of SNP-3 increases p65 protein levels in the nuclear fraction, indicating elevated NF-kappa B activation. Figure C: Activation of NF-kappa B after expression of a trafficking impaired transmembrane protein (Tmp; view total cell Lysate) and cellular stress revealed by elevated nuclear p65 protein levels (Nuc). M: mutant protein. wt: wild type protein. Cyt: cytoplasmic fraction.
|
|
Product Citations*
|
Safety, Storage, Shipping, NF-kappa B Activation Assay Kit, Part No. NFKB-2
Safety: Irritant. Avoid ingestion, eye and skin contact, and inhalation. Use in ventilated areas.
Storage: p65 Antibody: Aliquot, -20oC. HRP antibody, 4oC. Other contents at -20oC.
Recommended Shipping. Ships at ambient temperature. Domestic overnight and 2-day delivery and international priority delivery are available, Fully stable for international shipping to Canada, Europe, Asia, Middle East, and South America at ambient temperature.
kw. NFKB, NF-kappa b, NF-KAPPAB, ASSAY, p65 activation assay, kit, NF-KB, NUCLEAR FACTOR
| Category | Download Link |
| Protocol Manual | click here |
|
p65 Antibody Data Sheet |
click here |
|
Addendum for Tissues |
click here |
| MSDS | click here |
 Products
Products Manuals
Manuals





 ELISA Kit - FIVEphoton Biochemicals copy-80x80.jpg)