LEPTIN ELISA KITS (96T: Human # 27775, Mouse # 27160, Rat # 27160)
 Click to enlarge |
|
HUMAN LEPTIN ELISA KIT
| Conjugate | HRP |
|---|---|
| Species | Human |
| Measuring Samples | Serum, EDTA-plasma, Cell culture supernatant |
| Measurement Range | 15.63 ~ 1,000 pg/mL |
| Primary Reaction | 60 minutes at 37℃ |
| Secondary Reaction | 30 minutes at 2 - 8℃ |
| Sensitivity | 2.13 pg/mL |
| Specificity |
Compound Cross Reactivity Human Leptin 100.0% Mouse Leptin 2.4% Rat Leptin ≦ 0.1 |
| Storage Condition | 2 - 8 ℃ |
|
Leptin is a hormone primarily produced by fat cells (adipose tissue). Here's a breakdown of what leptin does:
Leptin Levels:
The amount of leptin in the bloodstream is directly proportional to the amount of body fat.
Leptin Resistance:
In some individuals, particularly those with obesity, a condition known as leptin resistance can develop.
In summary, leptin is a vital hormone that helps regulate energy balance in the body. .___________________________________________________________________________________________________
Storage: 4oC, 1 year
Safety: Stop solution contains acid. Avoid contact, wear eye protection.
Shipping: Overnight delivery with styrofoam box and ice packs. International delivery is also available: Please inquire for costs.
|
 Products
Products Manuals
Manuals
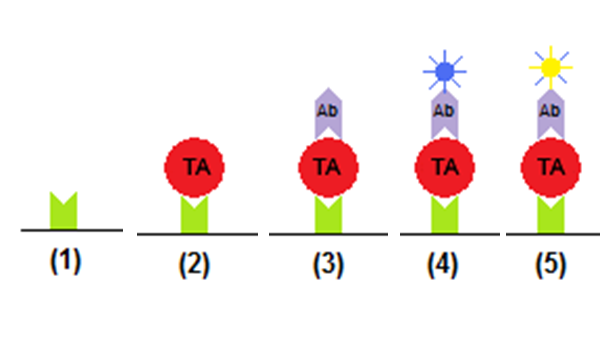 Methods Overview
Methods Overview