p65(RelA) Translocation Assay Kit (Part No. p65-Trans)
 Click to enlarge |
|
-
Rapid, quantitative assay to measure p65 translocation from cytoplasm to nucleus.
-
Generates nuclear fraction with concentrated p65 protein.
-
Applicable for most mammalian cells.
-
Data displayed in Images and Data tab
-
Cytoplasmic Fractionation Reagent (CER-1; 55 ml)
- Nuclear Fractionation Reagent (NER-1; 3.5 ml)
- DTT (sufficient to make a 1M solution with a volume of 64 microliters)
- Rabbit Polyclonal IgG Antibody to p65. 100 microliters provided: Use at 1:100- 1:400 dilution for Western blots
Data displaying p65(RelA) translocation; click "Images and Data" tab
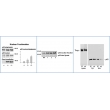
Figure Legends: All data derived from transfected HEK293 cells. First Figure: Western blot and quantitative analysis revealing NF-kappa B activation and p65 translocation as determined from three experimental repetitions elicited by transfection and overexpression of SNP variants of a gene associated with a neurological disease. Lane 1 in the Western blot and the corresponding bar chart reflect the mock transfection control (nl). Lane 2 in the Western blot and the corresponding bar chart reveal expression of the mutant variant SNP-1 (S1) of the gene. Lane 3 in the Western blot and the corresponding bar chart reveal the p65 translocation response to expression of SNP-2 (S2). Western blot data display elevated levels of p65 subunit protein in the nuclear fraction corresponding to expression of SNPs 1 and 2, demonstrating cellular stress and NF-kappa B activation. Second Figure: In an independent and repetitive experiment to that displayed in Figure 1, data revealing elevated translocation of p65 into the nuclear fraction following transfection of SNP variants 1 to 3 of the gene associated with a neurological disease (relative to expression of the wild-type variant; WT). Comparisons were done with p65 protein levels in nuclear fractions relative to p65 levels in total cell lysate. Transfection of SNP-3 increases p65 protein levels in the nuclear fraction, indicating elevated NF-kappa B activation and cellular stress. Third Figure: Activation of NF-kappa B and p65 translocation after expression of a trafficking impaired transmembrane protein (Tmp; displayed in total cell Lysate) and activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress as revealed by elevated p65 protein levels in the nuclear fraction (Nuc). Legend: M: mutant protein. wt: wild type protein. Cyt: cytoplasmic fraction. Nuc: nuclear fraction.
The assay isolates a nuclear fraction with concentrated p65, as well as a cytoplasmic fraction. To separate cytoplasmic from nuclear fraction, cells are first exposed to the "Cytoplasmic Fractionation Reagent (Part CER-1)." The cell suspension is briefly centrifuged in a microcentrifuge, which generates the cytoplasmic fraction in the supernatant. A resulting pellet is washed in the Cytoplasmic Fractionation Reagent and then extracted with the "Nuclear Fractionation Reagent (Part No. NER-1)." Aliquots of each fraction are resolved in Western blots, with consecutive lanes loaded to display total cell lysate, cytoplasmic fraction and nuclear fraction. The extent of p65 translocation from the cytoplasm into the nucleus provides a quantitative estimate of NF-kappaB activation.
Antibody to p65(RelA) for Western blots
Antibody to p65 for Western blot is included in this kit in 100 microliter aliquots (rabbit polyclonal, IgG; applicable at 1:400 dilution. The antibody is reactive toward human, mouse, hamster, rat, canine, bovine, porcine and equine p65. Use anti-rabbit IgG-HRP to detect the anti-p65 antibody on Western blots). See Images and Data tab for examples of reactivity of the provided p65 antibody
Icon Image: Structure of NF-kB p65-p50 heterodimer bound to PRDII element of ß-interferon promoter, PDB: DOI:10.2210/pdb2i9t/pdb NDB ID: PD0866.
Product Citations (identical to kit Part NFKB-2)
-
Bhatti, F.U.R., Hasty, K.A. & Cho, H. Inflammopharmacol (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-018-0542-5. Link to article
-
Das, N., Dewan, V., Grace, P.M., Gunn, R.J., Tamura, R., Tzarum, N., Watkins, L.R., Wilson, I.A. and Yin, H., 2016. HMGB1 Activates Proinflammatory Signaling via TLR5 Leading to Allodynia. Cell Reports, 17(4), pp.1128-1140. Link to article
-
Dattaroy, D et. al.2015. Micro-RNA 21 inhibition of SMAD7 enhances fibrogenesis via leptin-mediated NADPH oxidase in experimental and human nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Vol.no. DOI:
-
, X-Y, et. al. 2014. Glyoxalase I Is Differentially Expressed in Cutaneous Neoplasms and Contributes to the Progression of Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Journal of Investigative Dermatology (3 September 2014) | doi:10.1038/jid.2014.377. Link to article
-
Jae-Won Lee, J-W., 2013. Aromadendrin Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Nuclear Translocation of NF-κB and Phosphorylation of JNK in RAW 264.7 Macrophage Cells. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2013 May 30; 21(3): 216–221. Link to article
-
, , , and TAT-Hsp70 induces neuroprotection against stroke via anti-inflammatory actions providing appropriate cellular microenvironment for transplantation of neural precursor cells. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism 33, 1778-1788 (November 2013). Link to article
-
Musa Mulongo et. al. 2013. In vitro infection of bovine monocytes with Mycoplasma bovis delays apoptosis and suppresses production of IFN-γ and TNF-α but not IL-10.
-
Huang Z, Rose AH, Hoffmann FW, Hashimoto AS, Bertino P, Denk T, Takano J, Iwata N, Saido TC, Hoffmann PR. 2013.
Calpastatin Prevents NF-κB–Mediated Hyperactivation of Macrophages and Attenuates Colitis. J. Immunol. 2013 Oct 1;191(7):3778-88. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1300972. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Link to article
-
Amelia A. Romoser et al. 2011. Quantum dots trigger immunomodulation of the NFκB pathway in human skin cells. Mol Immunol. 2011 July; 48(12-13): 1349–1359. Link to article
References, p65(RelA) Translocation
-
Fazal F, Bijli KM, Minhajuddin M, Rein T, Finkelstein JN, Rahman A. 2009. Essential role of cofilin-1 in regulating thrombin-induced RelA/p65 nuclear translocation and intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) expression in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 284: 21047-56.
-
Fazal F, Minhajuddin M, Bijli KM, McGrath JL, Rahman A. 2007. Evidence for actin cytoskeleton-dependent and -independent pathways for RelA/p65 nuclear translocation in endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 282: 3940-50.
-
Lim JW, Kim KH, Kim H. 2008. NF-kappaB p65 regulates nucleartranslocation of Ku70 via degradation of heat shock cognate protein 70 in pancreatic acinar AR42J cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40: 2065-77.
-
Loveridge CJ, MacDonald AD, Thoms HC, Dunlop MG, Stark LA. 2008. The proapoptotic effects of sulindac, sulindac sulfone and indomethacin are mediated by nucleolar translocation of the RelA(p65) subunit of NF-kappaB. Oncogene 27: 2648-55.
-
Mattioli I, Sebald A, Bucher C, Charles RP, Nakano H, et al. 2004. Transientand selective NF-kappa B p65 serine 536 phosphorylation induced by T cell costimulation is mediated by I kappa B kinase beta and controls the kinetics of p65 nuclear import. J Immunol 172: 6336-44.
 Products
Products Manuals
Manuals
 ELISA Kit - FIVEphoton Biochemicals copy-80x80.jpg)
 ELISA Kit - FIVEphoton Biochemicals-80x80.jpg)
 ELISA Kit - FIVEphoton Biochemicals-80x80.jpg)